Ragas
Inicio rápido
Concepción
| 概念 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Question | |
| Contexts | Retrieved contexts:实际找到的Context |
| Answer | 最终生成的答案 |
| Ground truths | 参考答案 |
Dataset
from datasets import Dataset
data_samples = {
'question': ['When was the first super bowl?', 'Who won the most super bowls?'],
'answer': ['The first superbowl was held on January 15, 1967', 'The most super bowls have been won by The New England Patriots'],
'contexts' : [['The Super Bowl....season since 1966,','replacing the NFL...in February.'],
['The Green Bay Packers...Green Bay, Wisconsin.','The Packers compete...Football Conference']],
'ground_truth': ['The first superbowl was held on January 15, 1967', 'The New England Patriots have won the Super Bowl a record six times']
}
dataset = Dataset.from_dict(data_samples)
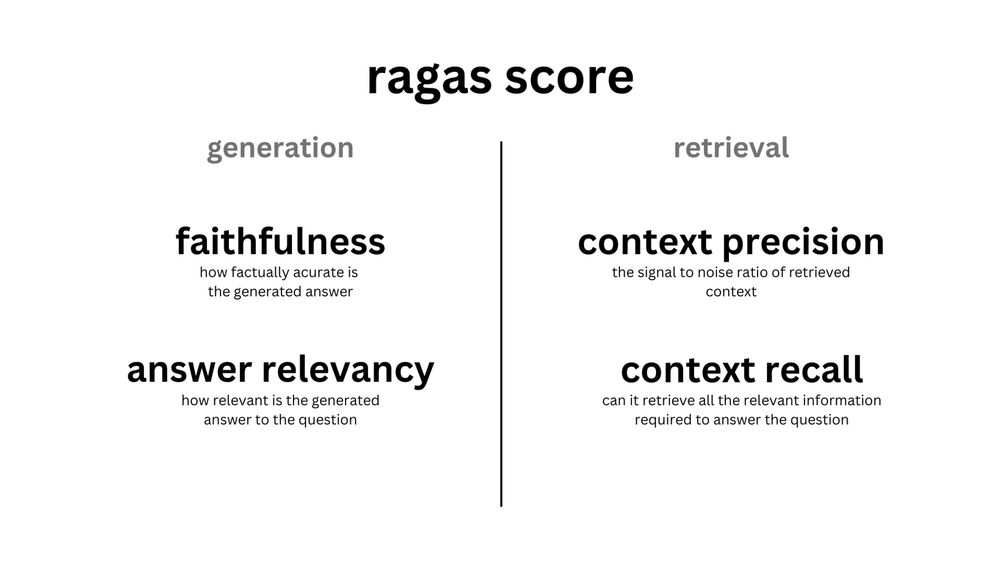
Métrica
| Metric | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Context Precision | Retrieval | Question | 是否跑题:检索结果 与 Quesion 是否相关 |
| Answer Relevance | Anwser | Question | 是否跑题:生成的答案 是否与 Question 相关 |
| Faithfulness | Anwser | Retrieval | 是否参考引用:生成的答案 是否忠诚于 检索结果 |
| Context Recall | Retrieval | 参考答案 Ground Truth | 检索的准确性: 检索结果 与 参考答案 是否相关 |
Pronto
Contexto de precisión
Given question, answer and context verify if the context was useful in arriving at the given answer. Give verdict as "1" if useful and "0" if not with json output.
The output should be a well-formatted JSON instance that conforms to the JSON schema below.
……
Your actual task:
question: 法国的首都是什么?
context: 巴黎是法国的首都。
answer: 巴黎
verification:
Respuesta Relevancia
No entiendo el prompt
Generate a question for the given answer and Identify if answer is noncommittal. Give noncommittal as 1 if the answer is noncommittal and 0 if the answer is committal. A noncommittal answer is one that is evasive, vague, or ambiguous. For example, "I don't know" or "I'm not sure" are noncommittal answers
……
Your actual task:
answer: 巴黎
context: 巴黎是法国的首都。
output:
La fidelidad
Create one or more statements from each sentence in the given answer.
……
Your actual task:
question: 法国的首都是什么?
answer: 巴黎
statements:
Your task is to judge the faithfulness of a series of statements based on a given context. For each statement you must return verdict as 1 if the statement can be verified based on the context or 0 if the statement can not be verified based on the context.
……
Your actual task:
context: 巴黎是法国的首都。
statements: ["\u6cd5\u56fd\u7684\u9996\u90fd\u662f\u5df4\u9ece\u3002"]
answer:
Contexto de recuerdo
Given a context, and an answer, analyze each sentence in the answer and classify if the sentence can be attributed to the given context or not. Use only "Yes" (1) or "No" (0) as a binary classification. Output json with reason.
……
Your actual task:
question: 法国的首都是什么?
context: 巴黎是法国的首都。
answer: 巴黎
classification:
Generación de datos compuestos
Motivación: La creación manual de cientos de muestras de QA (pregunta-contexto - respuesta) a partir de un documento puede ser lenta y laboriosa. Utilice LLM para generar automáticamente
Dividido en varias categorías: simple, * * razonamiento, condicionamiento, multi-contexto**
Estas categorías se llaman: * * Evoluciones * *
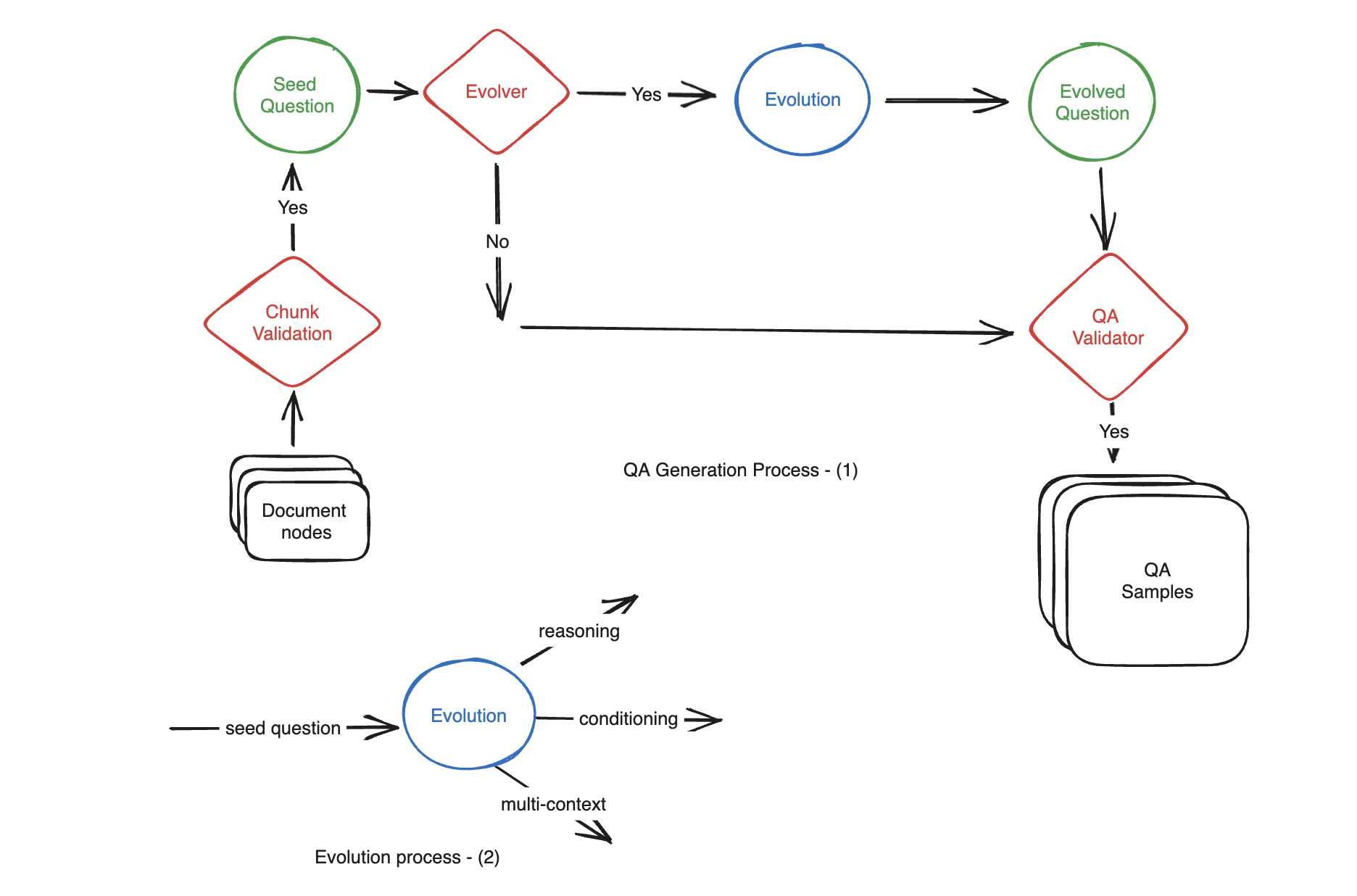
Al generar, especifique las proporciones de las tres categorías.
from ragas.testset.generator import TestsetGenerator
from ragas.testset.evolutions import simple, reasoning, multi_context
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
# documents = load your documents
# generator with openai models
generator_llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-16k")
critic_llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4")
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
generator = TestsetGenerator.from_langchain(
generator_llm,
critic_llm,
embeddings
)
# Change resulting question type distribution
distributions = {
simple: 0.5,
multi_context: 0.4,
reasoning: 0.1
}
# use generator.generate_with_llamaindex_docs if you use llama-index as document loader
testset = generator.generate_with_langchain_docs(documents, 10, distributions)
testset.to_pandas()
Leer los datos
No es fácil tener problemas con el uso oficial de LangChain y el uso continuo de LangChain.
Adaptación automática del idioma
Evaluación
El Prompt utilizado durante la evaluación se tradujo al chino utilizando el modelo gpt - 4 - turbo-preview; almacenado en caché localmente.
Las indicaciones pertenecientes a las métricas respectivas se adaptarán automáticamente al idioma de destino.
El paso de guardar lo guarda en
.cacha/ragaspor defecto para reutilizarlo más tarde.
# 将Metric中的Prompt翻译成中文
from datasets import Dataset
# from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAI
from ragas.metrics import (
answer_relevancy,
faithfulness,
context_recall,
context_precision,
answer_correctness,
answer_similarity,
)
from ragas import evaluate
from ragas import adapt
eval_model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0)
# llm used for adaptation
openai_model = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-4-turbo-preview")
# openai_model = OpenAI(model_name="gpt-4-0125-preview", temperature=0)
adapt(
metrics=[
answer_relevancy,
# faithfulness,
context_recall,
context_precision,
answer_correctness,
# answer_similarity,
],
language="Chinese",
llm=openai_model,
)
# Eval
dataset = Dataset.from_dict(
{
"question": ["法国的首都是什么?"],
"contexts": [["巴黎是法国的首都。"]],
"answer": ["巴黎"],
"ground_truths": [["巴黎"]],
}
)
print(dataset)
results = evaluate(dataset, llm=eval_model)
print(results)
Datos cachés generados

Generación de datos compuestos
from ragas.testset.generator import TestsetGenerator
from ragas.testset.evolutions import simple, reasoning, multi_context,conditional
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
# generator with openai models
generator_llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-16k")
critic_llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4")
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
generator = TestsetGenerator.from_langchain(
generator_llm,
critic_llm,
embeddings
)
# adapt to language
language = "Chinese"
generator.adapt(language, evolutions=[simple, reasoning,conditional,multi_context])
generator.save(evolutions=[simple, reasoning, multi_context,conditional])
Datos cachés generados

Campos en un dataset
- Pregunta
- contexts: el contexto recuperado
- ground _ truth: Respuesta de referencia
- anwser: respuestas generadas
- Question: A set of questions.
- Contexts: Retrieved contexts corresponding to each question. This is a
list[list]since each question can retrieve multiple text chunks. - Answer: Generated answer corresponding to each question.
- Verdades fundamentales: Verdades fundamentales que corresponden a cada pregunta. Esta es una
stringque corresponde a la respuesta esperada para cada pregunta.
Contexto de referencia no utilizado por el momento
metrics=[
# 这几个都不需要原始的context
context_precision,
answer_relevancy,
faithfulness,
context_recall,
],
Utilización de BGE
from ragas.llama_index import evaluate
flag_model = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(model_name="BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5")
query_engine2 = build_query_engine(flag_model)
result = evaluate(query_engine2, metrics, test_questions, test_answers)
Integración LangSmith
Establecer variables ambientales
export LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2=true
export LANGCHAIN_ENDPOINT=https://api.smith.langchain.com
export LANGCHAIN_API_KEY=<your-api-key>
export LANGCHAIN_PROJECT=<your-project> # if not specified, defaults to "default"
Crear un rastreador
# langsmith
from langchain.callbacks.tracers import LangChainTracer
tracer = LangChainTracer(project_name="callback-experiments")
Utilizado durante la evaluación
from datasets import load_dataset
from ragas.metrics import context_precision
from ragas import evaluate
dataset = load_dataset("explodinggradients/amnesty_qa","english")
evaluate(dataset["train"],metrics=[context_precision],callbacks=[tracer])
Integración LlamaIndex
官方文档有问题。